Difference between revisions of "SNParrayDB"
(→Using SNParrayDB) |
(→Link) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Link== | ==Link== | ||
| − | The Crop SNParrayDB can be accessed here: http://snpdb.appliedbioinformatics.com.au | + | The Crop SNParrayDB can be accessed here: http://snpdb.appliedbioinformatics.com.au/ |
==Using SNParrayDB== | ==Using SNParrayDB== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
===Scan a genomic region for SNPs=== | ===Scan a genomic region for SNPs=== | ||
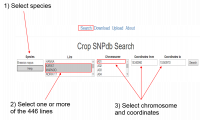
A comparative search query between the cultivars Karat and Marnoo for SNPs in a region of chromosome A01 can be carried out from the landing page, by inputting species, lines, chromosome and coordinates (Fig. 1). | A comparative search query between the cultivars Karat and Marnoo for SNPs in a region of chromosome A01 can be carried out from the landing page, by inputting species, lines, chromosome and coordinates (Fig. 1). | ||
| − | [[File:CropSNPdb_Search.png|200px|thumb|'''Figure 1''' Overview of the Search page for querying SNPs]] | + | [[File:CropSNPdb_Search.png|200px|thumb|right|'''Figure 1''' Overview of the Search page for querying SNPs]] |
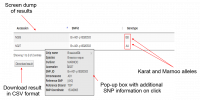
The search result is dumped to the screen in tabular format. Additional information on the SNP can be accessed by clicking on the SNP row, which brings up a pop-up box with all additional SNP metadata (Fig. 2). | The search result is dumped to the screen in tabular format. Additional information on the SNP can be accessed by clicking on the SNP row, which brings up a pop-up box with all additional SNP metadata (Fig. 2). | ||
Latest revision as of 09:47, 26 November 2018
Contents
Introduction
Advances in sequencing technology have led to a rapid rise of available genomic data for plants, driving new insights into the evolution and domestication of crops. Single nucleotide polymorphisms are a major component of crop diversity and are invaluable as genetic markers in breeding programs. To address the lack of SNP data provided by major databases and to make this data more easily accessible to researchers and breeders, we have developed SNParrayDB, the first database which focuses on SNP array data from oilseed rape (Brassica napus) and bread wheat (Triticum aestivum). SNParrayDB is a comprehensive web-portal providing a database of large-scale genome variation from the Brassica 60K Illumina Infinium™ array for 446 lines from 19 countries and from the Infinium iSelect Wheat 90k array for 309 lines. We include data from three recently published SNP assay datasets (Mason et al., 2015; Qian et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2016) and provide search, download and upload utilities for users. SNParrayDB is a useful starting point for a range of genomics and molecular breeding activities for oilseed rape and wheat.
Link
The Crop SNParrayDB can be accessed here: http://snpdb.appliedbioinformatics.com.au/
Using SNParrayDB
Scan a genomic region for SNPs
A comparative search query between the cultivars Karat and Marnoo for SNPs in a region of chromosome A01 can be carried out from the landing page, by inputting species, lines, chromosome and coordinates (Fig. 1).
The search result is dumped to the screen in tabular format. Additional information on the SNP can be accessed by clicking on the SNP row, which brings up a pop-up box with all additional SNP metadata (Fig. 2).
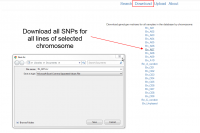
Bulk download SNPs by chromosome
Users can download all canola genotypes hosted by the database by chromosome as comma-delimited tabular files (Fig. 3).
Submit SNPs
User can upload their own oilseed rape SNP array data using the submission portal of Crop SNParrayDB (Fig.4). A genotype matrix and a list of line names and accessions should be uploaded. Example files with correct formatting can be downloaded from the page.
References
- Mason AS, Zhang J, Tollenaere R, Vasquez Teuber P, Dalton-Morgan J, Hu L, Yan G, Edwards D, Redden R, Batley J. 2015. High-throughput genotyping for species identification and diversity assessment in germplasm collections. Mol Ecol Resour 15(5): 1091-1101.
- Qian LW, Qian W, Snowdon RJ. 2014. Sub-genomic selection patterns as a signature of breeding in the allopolyploid Brassica napus genome. BMC Genomics 15.
- Xu LP, Hu KN, Zhang ZQ, Guan CY, Chen S, Hua W, Li JN, Wen J, Yi B, Shen JX, et al. 2016. Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic architecture of flowering time in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). DNA Research 23(1): 43-52.
- The Triticeae Toolbox (T3) (http://triticeaetoolbox.org/)
Back to main page